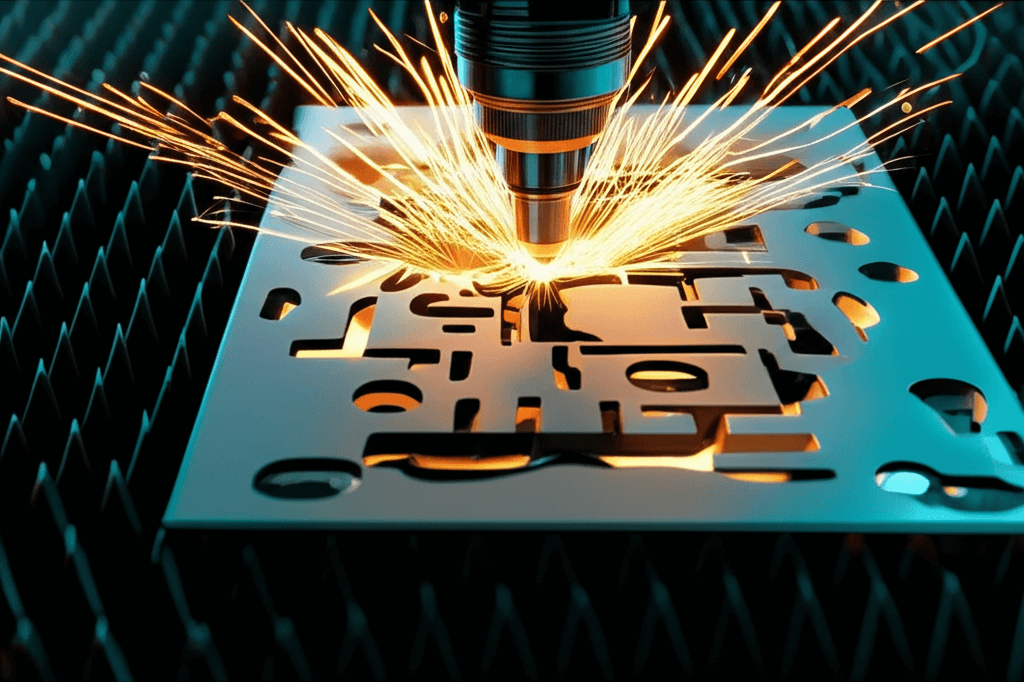
Laser cutting is a production method that uses concentrated light energy to cut materials with high precision. This technology has become indispensable in many industries today. Especially in the metal industry, it significantly increases production quality thanks to the ability to cut sheet metal, plastic, wood, acrylic, and fabric in different materials without any problems and cleanly. The non-contact cutting method of the laser, which does not create physical friction, minimizes deformation in the parts and makes it possible to produce more aesthetic and durable products.
Today, laser cutting is preferred in a wide range of areas from automotive to textile, furniture to electronics industry. The main reasons for this are advantages such as high speed, flexibility, low waste rate and repeatability. In addition, the flexibility it provides in the production of complex patterns, detailed internal hollowing out or micro parts offers a much superior performance compared to traditional cutting methods. This makes laser cutting one of the indispensable parts of modern production lines.
Savings in Time and Cost
One of the biggest advantages of laser cutting systems is the speed and time savings it provides in the production process. Thanks to CNC control systems, cutting processes are carried out automatically with predefined programs. In this way, human error is minimized and cutting times are significantly shortened. Especially when it comes to mass production, laser technology can cut more than one piece at a time flawlessly. This means not only a time saving but also a significant decrease in production costs.
Laser machines, which are also efficient in terms of energy consumption, use less electricity than classical mechanical cutting equipment. In addition, laser cutting contributes positively to the overall production budget by reducing labor costs and eliminating the need for additional processes such as molding or drilling. This creates a sustainable production model for businesses of all sizes, from small workshops to large industrial facilities. Especially in variable orders and low-volume production, the absence of mold costs offers companies great flexibility.
Cutting Quality and Precision
One of the most prominent features of laser cutting processes is their ability to work with high precision. These systems, which can work with tolerances below millimeters, allow even complex geometric shapes to be cut clearly, smoothly and without burrs. This makes a big difference, especially in projects that require fine workmanship. In addition, laser-cut parts usually do not require additional processing, meaning there is no need for operations such as sanding, grinding or a second cut.
In addition to precision, the surface quality is also quite high. There are no deformations such as burn marks, burrs or melting on the cut surface. This makes laser cutting particularly attractive for products where aesthetic appearance is important. Thanks to high-quality optical systems and advanced CNC software, every part can be produced with the same accuracy. Thanks to the thinness of the laser point, even the smallest details can be processed clearly. These features make laser cutting indispensable not only in production but also in design-oriented works.
Industrial Laser Cutting Technologies
Laser cutting technology can be applied with several different methods. The two most commonly used types of lasers are: CO₂ laser and Fiber laser systems. CO₂ laser is a gas-based laser type and generally produces excellent results in organic materials (wood, plastic, fabric, etc.). These systems produce high-quality surfaces, but their efficiency is limited in metal cutting. On the other hand, fiber lasers are solid-state lasers and are particularly effective in metal cutting. Thanks to their high light intensity, they provide deeper and faster cuts.
Different methods can be used during cutting: fission (melting), flame cutting and sublimation. These methods are preferred depending on the type and thickness of the material. While the fission method is generally preferred for high-quality cutting, flame cutting is used on thicker materials. Sublimation comes into play in more special applications.
All these processes are managed by CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems. Automatic cutting reduces human intervention and increases consistency. Especially in the mass production of complex and delicate parts, laser machines working integrated with CNC offer serious time and quality advantages. Thanks to this integration, digital production lines that are fully compatible with automation systems can be established.
Laser Cutting Services Offered at Depotaraf
Depotaraf Systems provides solutions to the needs of different sectors with the versatile services it offers in the field of laser cutting. The company successfully cuts metals such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, as well as plastic derivatives such as plexiglass, polycarbonate, PVCThis variety provides customers with project-based flexibility.
The machines used in Depotaraf are high-capacity and stand out in the sector in terms of maximum cutting dimensions and thickness capacities. For example, steel up to 20 mm and stainless steel up to 15 mm can be cut. In addition, large processing areas such as 3000x1500 mm are available for cutting large-sized sheet metal.
Precise adjustment of CNC parameters in cutting processes minimizes part tolerances. Optimized software is used in part layout planning to minimize material loss. In this way, both cost advantage is provided and production processes become more sustainable.
Quality and Precision in Laser Cutting
One of the most critical advantages offered by laser cutting is its ability to offer high quality and micron-level precision together. The laser beam used in these systems performs cutting with minimum heat transfer when focused on the material. This completely eliminates deformation, especially in thin materials that are prone to heat. The cutting edges are smooth, burr-free and clean. Thus, parts ready for assembly or use are obtained without the need for additional operations after the process.
Thanks to ultra-short pulse technology, micro-scale cutting is also possible. This technology allows the laser beam to be turned on and off at a speed of one millionth of a second, allowing very fine and delicate details to be processed with minimal heat dissipation. This technology is frequently used in sectors that require micron-level accuracy, such as electronics, the watch industry or delicate medical device parts.
In addition, the contour freedom offered by laser cutting, in other words, the easy production of even complex geometries, exceeds the limits of traditional production methods. Curved lines, internal cavities, detailed patterns or designs consisting of thin channels can be easily cut with the laser. This has paved the way for laser cutting not only in industrial but also in artistic projects. This technology, which removes design boundaries, turns every imaginable idea into a cuttable reality.
Laser Cutting and Mass Production
Laser cutting technology is an ideal solution for both low-volume prototyping projects and high-volume mass production lines. The main reason for this is the flexibility and speed of the system. Only a digital drawing file is needed to create a design on CNC-supported laser machines. This file can be loaded into the machine and the first prototype can be obtained within minutes. Going into production without mold or special equipment costs both speeds up and reduces the cost of R&D processes.This situation provides a great advantage especially for start-ups, special design companies and creative product development initiatives. Being able to test a large number of designs before the product is launched on the market makes it easier to achieve optimum results. At the same time, customizable production can be made according to customer requests, which also makes laser cutting stand out in individual and boutique production.
In terms of mass production, the fast cutting cycles and repeatable quality offered by lasers mean minimum errors and maximum efficiency in production lines. This system, which provides consistency between parts, reduces assembly errors and simplifies post-production quality control processes. Especially in high-volume orders, laser cutting becomes an unrivaled choice in terms of both time and cost.
Laser Cutting Machine Park & Technical Specifications
The success of laser cutting systems largely depends on the technical equipment of the machine park used. The basic determinants of the cutting process include the power of the laser, the focal diameter and the gases used. Laser powers, which generally vary between 2 kW and 12 kW, are preferred according to the thickness and type of the material. High-power lasers are used in thicker metals, while low-power ones are used in more precise cuts.
Cutting quality is increased by using gases such as oxygen, nitrogen and argon during the cutting process. For example, oxygen accelerates the cutting in materials such as carbon steel; nitrogen provides a smoother and oxide-free surface in materials such as stainless steel. Argon is preferred in more specific applications and completely prevents oxidation.
Cooling systems extend the life of the machine by preventing the laser source from heating up during long-term use and keep the cutting quality constant. While cutting accuracy is kept at the maximum level thanks to CNC control systems, optical equipment ensures that the laser light reaches the material in the most efficient way.
In terms of maintenance requirements, laser cutting systems can operate for a long time with simple processes such as regular cleaning, lens replacement and filter checks. In terms of work safety, light-proof cabins, emergency stop buttons and automatic sensors in the machines provide safety.It offers a high-quality production process. Thus, both operator health is protected and uninterrupted production can be provided in the enterprise.
Laser Cutting Applications: Sectoral Examples
Laser cutting technology is actively used in almost every sector thanks to its wide material variety and high precision. Especially in the furniture and decoration sector, cutting made with materials such as wood, MDF and plexiglass; allows modern, aesthetic and detailed designs to be realized. Laser-cut panels, lighting elements and special graphic patterns are frequently preferred in interior designs.
In the machinery and automotive sector, laser cutting has become an inseparable part of metalworking processes. Many elements from sheet metal to complex assembly parts, from chassis details to engine coatings are precisely cut with laser. Especially in these sectors where production speed and accuracy are important, laser technology guarantees both time savings and product quality.
While the construction sector increases the aesthetic value of architectural structures with laser-cut steel profiles and metal panels; In the white goods and electronics industry, laser cutting offers high efficiency in the production of internal assembly elements.
In addition, the contour precision and detail processing capability offered by laser cutting are at the forefront in textile, glass, ceramic and graphic design projects. For example, personalized products, souvenirs, logos and brand markings can be easily produced with laser. All these areas of use reveal how wide and effective laser cutting occupies both in the industry and design world.
Pricing and Cost Analysis
The pricing process in laser cutting projects varies depending on many technical factors. One of the most important elements is the thickness and type of the material to be cut. While thick materials require more laser power and cutting time, thin materials can be cut faster and with lower energy. This directly affects the cost per unit. For example, there are serious differences in terms of time, energy and gas usage between the cutting of 2 mm thick stainless steel and 10 mm thick carbon steel.
In laser cutting processes, the relationship between laser power and material thickness is decisive. While thicker materials can be cut quickly with high-power lasers, low-power lasers are preferred for more precise cuts. However, the investment and operating costs of high-power machines are higher, which is reflected in the prices. At the same time, the cutting gases used (oxygen, nitrogen, argon) are also among the factors that affect the cost. Nitrogen cutting processes generally provide smoother surfaces, but are more costly than oxygen cutting.
When performing cost analysis, not only the cutting time, but also the waste rate per piece, layout planning and material usage efficiency should be taken into account. The waste rate shows how much of the material used is considered as a product. These wastes can be minimized with optimum layout plans made with smart software, which reduces costs in the long term.
Labor and labor costs are also quite low in laser cutting systems. CNC-controlled machines require minimal operator intervention, which reduces personnel expenses. This quality-price balance offered by laser cutting allows businesses to offer high-accuracy products at affordable prices. Especially in high-volume orders, unit prices drop significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions About Laser Cutting
- On which materials does laser cutting give the best results?
Laser cutting gives excellent results especially on metal (steel, aluminum, stainless), plexiglass, MDF, wood and plastic materials. When the correct laser power and gas settings are used for each material, deformation-free and clean cuts are obtained. - How does cutting speed change according to thickness?
Laser cutting speed decreases as the material gets thicker. Thin sheets are cut faster, while thick parts are processed slower. Therefore, thickness is an important cost and time factor in project planning. - Is laser cutting harmful to the environment?
When the correct filtering and emission systems are used, laser cutting does not harm the environment. However, it is important to filter the fumes that come out when cutting plastic types. These systems work integrated in modern machines. - Will the material be damaged during cutting?
No. Since the laser beam cuts without contact, it does not cause physical deformation. However, if the wrong parameters are used, problems such as burning or melting may occur. Therefore, it requires expertise. - Is laser cutting or plasma cutting more advantageous?
Laser cutting is much more advantageous than plasma cutting in terms of precision, surface quality and low waste. However, for thick materialsPlasma cutting can be faster in applications. The choice should be made according to the type of application.